How to remove a keloid scar on the chest. Keloid scars: causes and treatment. Treatment of keloid scars with physical and physiotherapeutic methods
A colloidal scar is a type of scar that represents a pathological change in the healing process of a wound. A tumor-like formation is formed, which can sometimes reach impressive sizes.
Trying to find out why he was dangerous, doctors came to the consensus that he did not pose a danger to life and health. Being in an open place, a colloidal scar greatly reduces a person’s external attractiveness. With large sizes, it becomes a serious cosmetic problem.
Sometimes, when you press on the scar, pain occurs. If it is located in an area where it comes into contact with clothing, the person feels discomfort and begins to scratch the scar.
It is not uncommon for colloidal scars to prevent a person from moving normally. In all these cases, treatment is recommended.
The reasons for their occurrence
The reasons for the appearance of these formations have been studied by science for a long time, but doctors have not yet been able to determine the clear reasons for their appearance. At this stage, scientists have discovered several common prerequisites and conditions for the appearance of a scar.
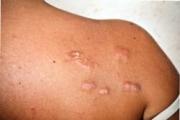
 Photo: colloid scars on the back
Photo: colloid scars on the back In this regard, the distribution of keloids into primary and secondary has been identified:
Primary or spontaneous
They occur for no obvious reason; either there were no wounds on the skin, or they were treated, but final healing did not occur. Colloidal scars can occur due to hormonal disorders, chronic infectious diseases, adrenal hypofunction, and pregnancy. Genetic predisposition may also be a cause. A connection has been noted with a predisposition to seborrhea.
Secondary scars
These keloids are a complication after injury or other skin diseases.
 Photo: scar on earlobe
Photo: scar on earlobe During the wound healing process, inflammation, suppuration, stress and weakened immunity may occur. All this disrupts the natural course of healing, the regeneration process goes wrong. Doctors have noticed that most colloid scars occur in the first six months after injury.
Quite often, scars appear at the site of burns; this happens within the first three months. Keloids are also not uncommon in women who have cosmetic problems.
They can occur after rhinoplasty, improper removal of a mole, or after permanent makeup that was performed incorrectly, or due to failure to follow safety precautions after the procedures.
In recent years, more and more young people and children are suffering from the disease, which is associated with frequent injuries and age-related skin problems. Increasingly, a colloidal scar appears on the earlobe after piercing.
How to remove this formation?
There are several treatment methods. It all depends on how old the colloidal scar is.
 Photo: formation on the earlobe
Photo: formation on the earlobe - If it is not neglected and has formed recently, then you can get by with medications and folk remedies. Medicines are either smeared on the surface of the scar or injected into the tissue.
- If the formation is very large, surgery is performed.
- Surgical methods also include electroexcision (excision using an electric knife) and laser excision (excision using a laser). Surgical methods are necessarily accompanied by preliminary and subsequent treatment with medications.
- Until a few years ago, old formations were removed using radiotherapy, X-ray therapy and Bukki-rays. But recent studies have shown that long-term non-healing ulcers can form at the site of the keloid, which transform into a malignant tumor. If there are other treatment options for colloidal scars, it is better to avoid such procedures.
- A colloidal scar after mole removal can be smoothed using electrocoagulation. The essence of the procedure is to apply electric current to the scar tissue. Sometimes special bandages with silicone inserts help.
- The cryodestruction procedure is quite painful, but in combination with Bucca irradiation or microwave therapy it gives very good results.
- Hormonal therapy is also used to combat the problem.
As a rule, removal occurs using several methods simultaneously in order to consolidate the effect of the procedure and prevent the occurrence of a new formation at the wound site.
For example, the earlobe will first be treated with injections of diprospan or kenologa-40. In a month, laser or electrical surgery will be scheduled.
After the wound has healed, irradiation with Bucca rays or microwave therapy will be performed, and the patient will have to wear a pressure clip for a certain time. In addition, some other procedures will be prescribed to avoid relapse: phonophoresis, electrophoresis and others.
Video: Scar removal, laser scar removal
Laser removal
 Photo: laser scar removal
Photo: laser scar removal This treatment method can be used no earlier than 6-12 months after scar formation. Laser resurfacing of colloidal scars is carried out using a CO2 laser.
It will not be possible to completely remove the keloid, but it will become invisible. The advantage of this method is that the surrounding tissues are minimally injured.
It becomes flat and less noticeable, but it will take from 6 to 12 sessions of the procedure. Between sessions, intervals of 1-2 months are allowed.
Video: Laser removal of scars at Laserhouse
Laser treatment is combined with other methods:
- administration of steroids;
- applying a silicone plate;
- using ointments.
The cost of one procedure directly depends on the size of the colloidal scar. Approximate cost of a session for a 1 cm scar? will be about $10, the larger the scar, the higher the cost of the procedure. Session time ranges from 20 to 60 minutes.
Unfortunately, relapses after such treatment are not uncommon; sometimes new keloids form along the edges of the former scar.
Ointments and creams for colloidal scars
There are few of these products in pharmacies, and not all are effective. The drug must be prescribed by a doctor, because many drugs differ in the period of use after surgery and have many contraindications.
 Photo: kelofibrase cream
Photo: kelofibrase cream In this situation, unfortunately, there is a clear trend: the cheaper and more accessible the drug, the less effective it is. The following are considered good:
- kelofibrase scar cream;
- 1% hydrocortisone ointment.
 Photo: gel Lyoton-1000
Photo: gel Lyoton-1000 The Spenko gel plate is very effective, which is used to treat existing scars and as a means of preventing the formation of new ones. The plate must be worn constantly, removing only for washing 2 times a day. The total treatment period, depending on the situation, ranges from 2 to 4 months.
Self-adhesive bandages with silicone are more convenient and preferable; Swedish-made Mepitel and Mepiform are especially good. It's worth looking into Zeraderm Ultra Scar Cream, which can be used under makeup if the keloid is located on the face. This product is approved for use by children.
 Photo: Zeraderm Ultra scar cream
Photo: Zeraderm Ultra scar cream The drug is produced using the latest medical discoveries, has an anti-inflammatory effect, improves the energy potential of cells, and protects against the harmful effects of ultraviolet rays. The cream must be applied twice a day; the course of treatment depends on the situation and can last several months.
Treatment of colloidal scars with diprospan should be used only on the recommendation of a doctor; there is an impressive list of contraindications for this remedy.
Diprospan is introduced into the scar tissue by injection, has many side effects, and is prohibited for use by pregnant and nursing mothers. ScarGuard is a liquid that is applied to the scar with a brush and dries instantly. The result is a coating that protects the damaged area of skin and serves as a compression bandage.
 Photo: ScarGuard drug
Photo: ScarGuard drug ScarGuard contains large amounts of vitamin E and hydrocortisone, which promote rapid wound healing.
It can be used for treatment and for prevention if the patient has a predisposition. Contratubeks is sold in pharmacies without a prescription. Before use, it is also advisable to consult a doctor, but the effect of this drug is mild and has no special contraindications.
Healing occurs due to onion extract, heparin and allantoin, which are part of the gel.
 Photo: drug contratubes
Photo: drug contratubes This remedy can be used by pregnant and lactating women who need to remove colloidal scar after cesarean section. The product can be used by both adults and children who have developed a scar after BCG.
If the formation is old, the product is applied under a bandage, which lasts from 6 to 12 hours. in milder cases, the gel is simply rubbed into the surface of the scar. Treatment can last from two weeks to several months, depending on the situation. Our ancient ancestors knew how to get rid of such formations; they used lotions from plant decoctions for this purpose. Traditional healers recommend using camphor oil to treat it, which should be moistened with a cloth and applied to the scar as a compress.
You need to be treated in this way for one month. A tincture of larkspur roots, which is prepared as follows, also copes well with colloid scars.
The roots of the plant need to be washed, crushed and filled with water and alcohol in equal parts.
The medicine is infused for about a week in a dark place. Using the tincture you need to make compresses and bandages.
 You can treat with a mixture consisting of chamomile, calendula and nettle. 2 tbsp. l. The mixture should be poured with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for an hour. After this, you need to strain the infusion, soak a bandage in it and apply it to the scar for 3 hours. This should be done 2-3 times a day for 3 months.
You can treat with a mixture consisting of chamomile, calendula and nettle. 2 tbsp. l. The mixture should be poured with a glass of boiling water and allowed to brew for an hour. After this, you need to strain the infusion, soak a bandage in it and apply it to the scar for 3 hours. This should be done 2-3 times a day for 3 months.
An excellent remedy for colloidal scars is natural beeswax with olive oil.
To prepare the medicinal mixture, you need to mix 50 g of wax and 1 glass of olive oil. The mixture is heated in a water bath, mixed thoroughly and cooked for another 10 minutes.
The finished mixture needs to be cooled slightly, soaked in a piece of fabric and placed on the scar. This bandage is done twice a day for two months.
Keloid scars at the site of injury can form over many years, gradually changing. Conventionally, keloid scars are usually divided into fresh and old.
Fresh keloid scar- This is a scar that has existed for less than five years. It differs from old keloid scars in its bright color, glossy surface and active growth. Old scar- pale, wrinkled, soft.
This classification is very important, since the choice of treatment depends on the type of scar. And of course, Keloid treatment should be started as early as possible. The best time is before the scar appears.
And this is not sarcasm. Most often, the tendency to form a keloid scar can be noticed even before it appears. In order to determine whether you have it, look carefully at how small wounds heal: after shaving in men, after piercing the ears in women.
If a thin, light-colored scar forms that does not rise above the skin, you are probably safe. But you still need to monitor the healing of any wound very, very carefully, since there are cases when keloids begin to form, as they say, without warning.
Expert comment:
In order to make the scar as invisible and thin as possible, many preparations have been created, among which gels, ointments and silicone-based patches occupy a special place.
Laser resurfacing of post-acne scars.
What is silicone gel against keloid sutures
Silicone ointments, creams and gels, such as Zeraderm or Dermatix, containing 100% medical grade silicone, play a big role in the treatment of scars, including keloids.
A silicone-based gel or cream does not allow connective tissue to grow, and at the same time protects scars from external influences, as it creates a thin film on the surface of the scars. In addition, silicone ointment for keloids smoothes and softens the scar, which relieves itching and pain.
In addition to silicone preparations, Hydrocortisone is used to combat keloid scars. Hydrocortisone ointment for hypertrophic and keloid scars suppresses the activity of fibroblasts and collagen formation, which means it does not allow scars to grow.
There are also many combination drugs, such as Contratubeks, Kenalog, Elokom and others. In addition to silicone, they may include other active ingredients: zinc, vitamin E and others necessary to fight scars and quickly heal elements.
Expert opinion
Scar patches
Recently, so-called silicone patches, or plates, are increasingly being used to combat keloid scars. They are glued to the surface of the scar, and at the same time provide its protection from mechanical damage and exposure to silicone, which affects the resorption of keloid scars.
As a rule, people who are prone to the appearance of keloid formations need to start applying the patches immediately after the wound has healed and a Dense crust has formed. This is an excellent prevention against the proliferation of connective tissue and the appearance of ugly, rough scars.
However, modern silicone-based preparations can be used not only in case of danger of keloid disease, but also in the healing of any wounds and sutures, so that scarring is easier and the scar is thinner and less noticeable.
Video
How to determine whether a keloid scar is or not
You can get advice about scars and other additional information by calling:
in Moscow +7 495 723-48-38, +7 495 989-21-16,
in Kazan +7 843 236-66-66.
Make an appointment online to receive a 30% discount on your consultation. And by purchasing a clinic certificate, you can pay for any Platinental services with a 10% discount.
A keloid scar is a consequence of skin trauma with pathological growth of connective tissue. It occurs approximately six months after healing in the wound area. It can grow over the course of 2 years, after which it stabilizes. People between 10 and 30 years of age are more likely to develop keloids.
The pathology has virtually no effect on overall health and well-being; it only causes psychological discomfort and emotional distress.
It differs from a regular or atrophic (retracted) scar:
- pinkish or bluish tint (due to the large number of blood vessels);
- redness of the skin around;
- complete preservation of sensitivity;
- the appearance of pulsation, pain and itching (intensified by friction of clothing);
- the formation of tubercles and compactions.
Who should I turn to for professional help to get rid of the defect? If a keloid scar has formed, treatment is carried out by dermatologists, surgeons and physiotherapists.
Causes of keloid scars
When magnified, a keloid looks like a tortuous nodule of collagen. Pathological tissue tends to grow, affecting healthy cells of the dermis. The skin most prone to the formation of keloid scars is the face, hands, earlobes, neck and chest.
The exact cause of the pathology is still not known. It is noted that this type of scar can occur both with complex extensive injuries and with subtle injuries such as a pimple, injection and insect bite. There are known cases where, for unknown reasons, keloids form on healthy skin.
Why do moles form after removal?
Nevi and warts can be removed as planned, without hospitalization. This is a fairly simple operation for both the doctor and the patient. Sometimes a keloid scar forms. It appears due to the uncontrolled proliferation of connective tissue at the site of traumatic amputation.
This postoperative complication is not dangerous to health, but requires the attention of a doctor. When the first symptoms of a keloid scar appear, you should consult a dermatologist or surgeon. This type is often similar in appearance to a dangerous complication - basal cell infiltrating malignant tumor. It is almost impossible to distinguish one pathology from another without histological examination.
Who's at risk
Common factors that contribute to the formation of scar tissue include:
- family history, genetic predisposition;
- metabolic and immune processes disorders (diabetes mellitus, HIV, obesity, connective tissue diseases);
- young age, puberty, pregnancy;
- black race;
- chronic infections;
- long-term use of NSAIDs, corticosteroids and other systemic agents;
- herpes zoster, erysipelas, chicken pox.
Local reasons contributing to the formation of keloid are:
- inflammation and poor circulation in the area of injury;
- tattoos and piercings;
- skin pigmentation;
- traumatization of an already formed young scar, for example, by a foreign body;
- wound infection;
- burns and acne;
- healing of damage by secondary intention;
- improper alignment of skin edges.
Differences between keloid scars and hypertrophic ones
After an injury, the body undergoes a regeneration process. In this case, a regular flat scar forms on the surface of the skin in the area of the wound. Sometimes during healing it can suddenly begin to thicken, then a hypertrophic or keloid scar appears. These types of connective tissue growths have many differences:
Treatment methods for keloid scars
There are two methods for removing keloid scars: surgical and therapeutic. The overgrown connective tissue is surgically excised, followed by suturing of the skin edges. After the intervention, an inconspicuous, thin scar remains, which is easier to correct. The negative side of this method is the high probability of recurrence.
Other treatment methods are aimed at transitioning from the hypertrophic to the normotrophic form of the scar. As a result, the scar becomes less noticeable. Which removal route to choose is determined by a qualified doctor, taking into account the size, location, shape, and old age of the formation. It is most effective to combine several methods of therapy at the same time.
Drug treatment
It is impossible to remove keloids using drugs. Medicines can stop the growth and make the scar less noticeable. This therapy is also effective after surgical excision. The most commonly used medications include:
- Hyaluronic acid is the central substance that regulates the density of formation. Therefore, the drugs that contain it can soften tissue and lighten the scar. The most commonly used are enzyme agents (Lidaza, Ronidaza, Longidaza). Injections are made directly into the pathological area, in a course of 5 to 20 injections. More effective for young keloids.
- Interferon helps stop the proliferation of connective tissue. It increases local immunity, which helps stop scar growth. For the first two weeks, the drug is injected into the pathological area every day, and then 4 times a month.
- Corticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Diprospan, Prednisolone ) have a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Therefore, they are used to treat young keloids, the growth of which occurs with inflammation in the tissues. Most often, injections or electrophoresis are used to administer hormones.
Cryodestruction
It involves exposing the rumen to low temperatures. The procedure is carried out by freezing pathologically overgrown tissues, destroying their structure. To enhance the result, it is often used in combination with microwave therapy.
Laser resurfacing
Using a laser, a specialist can remove the part of the scar protruding above the skin layer by layer. In this case, evaporation of pathological tissues and sealing of blood vessels occurs. An erbium and neodymium laser is used to carry out the manipulation. The first affects only the superficial layers of the keloid, the second can penetrate to a depth of up to 8 mm.
Can help make the scar almost invisible. The disadvantage of the method is the cost. For example, one procedure to remove a scar on the face will cost approximately 6,000 rubles. The price depends on the clinic, the qualifications of the doctor, the number of necessary manipulations, the size and location of the formation.
Pressotherapy
This is compression of the area where the keloid has formed, with inhibition of microcirculation in the pathological area. Due to local ischemia, the production of connective tissue and collagen is reduced, and the growth of the keloid completely stops or slows down. The compression effect is achieved using elastic bandages. The bandage must be worn, almost without removing, for a year.
Physiotherapy
This type of treatment is used in conjunction with medication. To smooth out and stop the growth of the scar and destruction of its tissues, the following are suitable:
- apiphorelectrophoresis - exposure to ultrasound with the application of a small amount of bee venom, used to treat burn scars;
- infrared irradiation (Sollux and Minin lamps) and galvanization to treat infection, dry out and quickly heal the wound, with a predisposition to the formation of keloids;
- diadynamic therapy is used to prevent excessive development of collagen fibers;
- paraffin treatment and darsonvalization are performed during the wound healing period;
- phonophoresis, ultrasound therapy, infrared radiation, electrophoresis with 5% iodine, mud therapy - used after complete epithelization of the scar in the presence of a dense scar to absorb excess fibrous tissue;
- bukki therapy - activation of reverse development of the scar using x-rays;
- hirudotherapy - biologically active substances released when leeches are sucked on, promote the resorption of compacted tissues.
Correction with cosmetic procedures
Not very effective for keloids. Use is possible only in combination with other treatment methods. They help to slightly correct the appearance of the formation, only if it is no more than six months old. Cosmetologists offer:
- mesotherapy;
The sooner therapy begins, the better the result can be achieved. There is no universal way to treat keloid scars; only an integrated approach will help make the scar less noticeable and reduce the likelihood of relapse.
Local therapy products - ointments and medicinal dressings
Using gels and ointments, you can lighten and make scar tissue softer. Their use is comfortable and painless for the patient. To achieve the desired effect, treatment creams must be used for at least six months. The most popular local remedies include:
- Contractubex;
- Clearwin;
- Kelofibrase;
- Imoferase (also used for old scars);
- Dermatix (silicone based);
- Fermenkol (suitable for both adults and children);
- Solcoseryl;
- Hydrocortisone ointment.
Sometimes, to enhance the effect, ointments are applied in the form of cream dressings with the addition of Dimexide. It promotes deep penetration of the drug into the tissue. A similar result can be achieved using a gel silicone patch.
Treatment at home with folk remedies
There are many folk recipes for getting rid of keloid at home:
- Melt Vaseline in a water bath, add 5 g of mumiyo and 25 ml of water. Stir and keep on fire until the solution changes color. After this, remove the mixture from the stove and cool to room temperature. The resulting homemade ointment should be applied in a thin layer 1-2 times a day for at least 1.5 months.
- Grind the cabbage leaves in a blender. Mix in equal proportions with honey. Use the product at night as a compress.
- Lubricate the keloid scar 2-3 times a day with one of the following substances: lemon juice, sea buckthorn oil, apple cider vinegar, aloe juice, olive or camphor oil with honey and propolis, infusions or decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, geranium and nettle.
Keloids cannot be removed using folk remedies. But with regular use, they will help soften and make pathological tissue less noticeable. You can treat yourself at home only after consulting a doctor.
How to get rid of old scars
Keloids are considered old if they are more than 5 years old. By this time, the scars do not increase in size and have a pale tint and a wrinkled surface. Their treatment is complex and lengthy.
Old scars can disappear completely only through plastic surgery with skin grafting. Excision in combination with other treatment methods suitable for young scars (physiotherapy, ointments) helps to make the keloid less noticeable.
Let's sum it up
There are many methods for getting rid of keloid scars. To achieve the best effect from treatment, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. As a rule, the best results are achieved by combining several types of therapy.
Do you know firsthand about keloid scars? Have you tried some types of therapy? Do you know how to effectively and permanently remove scars? We will be glad if you leave a review and share your experience.
Many have heard about keloid scars and seen photos of them on the Internet, but few know what a colloid scar is and why it appears. Below we will talk about this phenomenon, you will see photos of scars and learn the causes and types of colloidal scars, as well as how to treat such formations on the body.
- 2 Classification of colloid scars
- 3 Why do colloid scars appear?
- 4 Symptoms of keloid scars
- 5 Possible consequences of this phenomenon
- 6 Diagnosis and clinical treatment
6.1 Physical measures
7 Traditional medicine against colloid scars
8 Preventive measures
Classification
Colloidal scars are divided into two main groups: true and secondary or false.
The first ones are formed without any mechanical impact on the skin. In most cases, for unknown reasons, they are located on the back, in the chest area, on the earlobes and neck. Scars rise 5-7 mm above the surface of the epidermis.
They are benign, smooth, painless and insensitive. During laboratory studies of true keloids, specialists find many collagen fibers in the collected material.
Secondary scars are formed as a result of injuries and thermal or chemical burns of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. In some cases, a keloid forms at the site of a boil, trophic ulcer or stoma.

Keloids are also classified by age. There are recently formed and old scars. Young scars have a bright color and a smooth glossy surface. Old keloids are distinguished by an abundance of connective tissue nodes, roughness and pale color. 5-6 years after the appearance of scars, they stop increasing in size.
Attention! It is necessary to distinguish a keloid from other skin neoplasms. If the emerging growth is soft, quickly increases and is accompanied by swelling of nearby tissues, then there is reason to suspect the development of tumor processes.
Description of colloidal scars and scars according to ICD-10 code
A colloidal scar (scar) is a visible formation on the skin resulting from uneven fusion of the edges of damaged tissue. The scar worsens the appearance, but does not pose a danger to human health. The likelihood of the tumor developing into a malignant one is quite low.

Scars can be caused by injuries or infectious pathologies.
The primary form of colloidal scar forms suddenly without damage to the skin. The process of forming secondary education takes place in three stages:
- Epithelization. It takes about ten days and is characterized by the appearance of a primary thin layer of epithelial cells.
- Swelling. Scar tissue forms. The process takes about a month depending on the size of the lesion.
- Seal. The density of the scar increases due to the formation of connective tissue. Capillaries disappear from the surface.

Scar formation occurs in several stages.
Primary and secondary scars have different origins and causes. Signs of their formation are determined by the following phenomena:
- skin itching;
- painful sensations on palpation;
- absence of hair and sweat glands in the location area;
- acquiring a red or bluish tint.
In case scars form in the neck, ears and back for no apparent reason, you should consult a doctor as they may require intensive care.
Reasons for appearance
To date, it has not been possible to identify the exact causes that cause the appearance of colloidal scars. It was possible to establish that when the normal regeneration process is disrupted, pathological fusion of damaged tissue begins.
Healing of wound surfaces is a long and complex process in which, in addition to the skin, the immune, circulatory and lymphatic systems are involved, so it is very important to choose an ointment that will help quickly heal wounds.
In a healthy person, recovery from a minor injury takes about 7 days; a major burn or laceration can take about a year to heal. During regeneration, a flat scar forms on the skin, which subsequently disappears. If at any stage the process of tissue restoration is disrupted, then the damaged surface begins to be covered not by a new layer of epidermis, but by connective tissue with a high collagen content. A colloidal scar is formed. It may continue to grow beyond the wound, even months or years after the wound has healed.

A characteristic feature of a keloid is the minimal relationship between the size of the scar and the severity of the initial injury. Often, scars form at the site of minor scratches or abrasions, injections, acne, or insect bites. In a small percentage of people, keloids form on healthy skin for unknown reasons.
In this case, scars most often form on inactive areas of the body:
- In the navel area;
- On the chest and in the collarbone area;
- Behind the ears and on the earlobes;
- At the base of the neck;
- On the shoulders and in the area of the shoulder blades.
What not to do if a colloid scar appears
Treatment of a keloid scar must begin immediately after its occurrence. As soon as the first symptoms of this type of formation appear, you must immediately contact a surgeon who will prescribe adequate treatment.
If you delay, the situation will only get worse. What not to do if you have a keloid??
- Self-medicate. This can have the opposite effect and accelerate the growth of the scar and increase the pain. You need to be especially careful with folk remedies;
- Do peelings in the scar area;
- Apply a tattoo to a scar, even for the purpose of camouflage;
- If there is a keloid on the earlobe, it is prohibited to pierce it. This will cause rapid growth of connective tissue;
- Carry out scar removal yourself or in a dubious clinic.
Symptoms and diagnosis
A keloid is a rough growth on the skin. Its dimensions can vary from a few millimeters to 30-40 centimeters or more. Due to the abundance of blood vessels, the scar differs in color from the surrounding epidermis. It is easy to diagnose keloid due to a number of characteristic symptoms:
- Red or brown color of the scar. The skin around it may be hyperemic due to the abundance of capillaries;
- Unlike a regular scar, a keloid does not lose sensitivity; pressing on it may be accompanied by pain;
- Itching and throbbing in the area of large scars.
Symptoms accompanied by physical discomfort in most cases bother the patient during the first 11-15 months from the onset of the keloid.
After this period ends, the scar, as a rule, enters an inactive stage. It gradually stops increasing in size, turns pale and loses pain. 1-2 years after formation, the keloid takes on the appearance of a rough, irregularly shaped scar.
Symptoms of keloid scars
Many people cannot distinguish between the symptoms of hypertrophic and keloid scars, but they differ both in appearance and in their localization. The following are characteristic of keloid formations:
- they increase slowly;
- pulsation is felt;
- there is itching;
- the formation hurts when pressed;
- the skin may turn blue or red;
- there are no sweat glands or hair follicles on the scar;
- Such scars form on the décolleté, ears, neck, shoulder blades or chest.
Who is at risk?
There are a number of factors that are prerequisites for the development of colloidal scars:
- Disorders of the reproductive and endocrine systems, hormonal imbalances in the body;
- Adolescence or old age;
- Suppression of the immune system: condition after organ or tissue transplantation, previous diseases, presence of the immunodeficiency virus;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Inflammatory processes, wound suppuration;
- Impaired blood supply and innervation of the tissues of the injured area, including as a result of ulcerative processes or burns.
Attention! Often colloidal scars form on the lip, earlobe, navel or wings of the nose as a result of punctures. Keloid in this area due to infection in the wound and subsequent inflammatory processes. If you decide to get a piercing, be sure to follow the rules of caring for it: treat it with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory ointment (zinc or boron), develop a puncture, wear items made of silver or medical steel.
Preventive measures
To avoid the occurrence of colloidal scars, the following recommendations must be followed::
- Avoid causing wounds. Especially if there is a hereditary predisposition to the formation of massive scars;
- Follow the doctor's recommendations in the postoperative period;
- Wear a bandage after surgery;
- Avoid visiting baths and saunas, and also do not heat the scar;
- Do not massage or damage the scar;
- Use ointments and medications prescribed by the doctor. Do not self-medicate;
- Protect the postoperative wound from contamination;
- If a wound becomes infected, immediately contact a surgeon for advice;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle (giving up bad habits, proper nutrition, healthy sleep).
Treatment
Since the reasons for the development of colloidal scars have not been established, there is no universal therapy. The specialist selects the treatment method individually depending on the manifestation of the pathology. Treatment includes conservative, that is, medication, therapy and surgical interventions.
Pharmacological treatment is used to eliminate keloids that formed less than 12 months ago. The following methods are used:
- Freezing raised scars and growths with liquid nitrogen – cryotherapy(CryoPharma, Wartner Cryo). Nitrogen affects the fluid in the tissues, which is found in large quantities in keloid formations. The disadvantage of this method is that cryotherapy can only remove the external manifestations of the scar. This method should be used as part of complex therapy;
- Corticosteroid injections into the affected area(“Prednisolone”, “Lorinden”). This hormone leads to a local reduction in collagen production and reduces the inflammatory process;
- Immunomodulators(“Interferon”, “Likopid”) are also injected intradermally, directly into the scar tissue. Injections are carried out once every two weeks for three months;
- Medicines to prevent tissue proliferation(“Ronidaza”, “Longidaza”, “Lidaza”). These are agents that are injected into the area next to the scar and prevent the keloid from affecting nearby tissue;
- Ointments against tissue scarring. Used as a preventive or auxiliary agent: “Kontraktubeks”, “Dermatix”, “Solcoseryl”.
Treatment of colloid scars also includes the use of physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Microwave electromagnetic effect on the affected area. Used to destabilize the water contained in the keloid tissue. It is recommended to use this method in conjunction with cryotherapy;
- Electrophoresis- administration of corticosteroids using electrical impulses;
- Magnetic wave therapy. Used exclusively as a preventative measure to stimulate rapid wound healing. It is used to treat patients with a hereditary predisposition to the formation of colloidal scars, weakened immunity and large wounds.
5-6 months after the formation of a keloid, cosmetic procedures can be carried out aimed at eliminating the effects of skin scarring:
- Laser therapy to remove small connective tissue nodes;
- Peels and scrubs to smooth the skin;
- Darsonvalization.
How to remove colloidal scar?
You can get rid of the scar using cryotherapy or surgery. In the first case, the drug is applied to the growth for a long time, after which the keloid is removed layer by layer. To completely eliminate it, 5 to 15 procedures are required.
Surgery involves complete excision of the overgrown connective tissue. Stitches are placed on the wound. If the scar was large, then skin grafting is recommended to prevent re-formation of the keloid.
Attention! After surgical removal of a keloid, there is a high risk of scar recurrence. Therefore, after surgery it is necessary to carry out physiotherapeutic and drug treatment.

It is worth considering that patients with true keloids are contraindicated for any surgical or injection treatment methods, as they can lead to the formation of new scars.
Surgeon E.I. Karpova talks about the dangers of aggressive therapeutic methods for people with primary colloid scars.
Treatment with traditional methods
Along with cosmetic procedures, medications and physiotherapy, traditional medicine recipes can be used to get rid of keloids.
Lemon juice is used to treat various skin pathologies, including colloid scars. They should be gently applied to the affected area and left for 30 minutes. Afterwards, rinse off the juice with warm water. The procedure should be carried out every day for 1-2 months.
Another effective remedy for improving blood and lymph circulation in the keloid area is a collection of chamomile, yarrow and nettle.
Herbs have an anti-inflammatory and restorative effect.
You need to mix a tablespoon of each plant and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. After 1-2 hours, dip a clean gauze bandage into the infusion, apply it to the keloid and leave for 1.5-2 hours. Treatment should be carried out within 60 days.
To moisturize the skin and improve blood microcirculation in the capillaries of the scar, you can apply honey to the affected area daily and massage for 10-15 minutes.
Attention! The use of traditional methods of combating keloids should be carried out in combination with the use of traditional medicine methods.
Physical methods
In some cases, it is necessary to resort to physical methods of influence - this is the most effective, but is already considered surgical intervention:


They have been trying to fight the problem of unaesthetic defects (scars) for a long time. Therefore, quite a lot of options for treating colloidal scars with folk remedies have also accumulated, and doctors prescribe them in certain situations, to enhance the effect of the main treatment or to prevent relapses.
But self-medication is strictly prohibited!
Stages of scar formation
Scar formation can last from several weeks to 1-1.5 years. It occurs in three main stages:
- Epithelialization- initial stage. Over the course of about two weeks, the area of skin thickens, becomes pinkish and slightly swollen, and acquires a pale pink color;
- Increase– the keloid begins to rise above the surface of the endometrium and acquires a brownish or bluish tint. This period lasts about a month;
- Seal– the keloid becomes rough to the touch, dense nodes of connective tissue may form in it.
As the scar grows, each new affected area of skin goes through these phases of keloid formation.
Traditional medicine against colloid scars
Of course, folk recipes can serve as a good addition to treatment keloid formations on the body. They will help disguise the scar, soften it and have a resolving effect. Traditional methods are also good as prophylaxis after physiotherapy or taking special medications. Here are just a few of them:
- against keloid formations, applications, lotions and compresses based on chamomile, woodlice, geranium, St. John's wort, fennel, mint, yarrow, and Japanese sophora are used. For example, for a compress based on wood lice, you need to take its leaves, compact them into a jar and fill them with sunflower oil. Then the jar is placed in a dark place for about a couple of weeks. Then they open it, filter the resulting infusion and apply it to the scar under a cotton pad for half an hour;
- sea buckthorn oil, as well as a mixture of olive oil and honey Great for improving blood microcirculation for keloid scars;
- scar tissue can be wiped with essential oils based on tea or rosewood, incense, rosemary or mint;
- take equal parts melon seeds and eggshells, chop everything and mix. Add vegetable oil, mix again and apply the resulting slurry regularly to the scar for 2 months;
- dilute the pea flour with milk to a dough-like consistency and place on the tripe, covering with film for an hour. It is recommended to carry out such procedures for about 2 months;
- cabbage can have a regenerating effect on such formations. To do this, you need to chop several leaves and combine them with a spoon of honey. Apply to the affected area as a mask for an hour;
- to get rid of small formations, take equal amounts of yarrow, knotweed, chamomile, nettle and St. John's wort, combine them and pour a glass of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours and apply to the affected area using a linen napkin;
- Grind the marshmallow root, pour a glass of water into a spoon and leave for 9 hours. Then use it as a lotion, this infusion has a resolving effect and helps against swelling;
- camphor oil helps treat relapses and can be used to prevent the disease. Soak a bandage or napkin with oil and apply it as a compress on the keloid scar for several hours;
- Wash the larkspur root well, chop it and add a mixture of alcohol and water in equal proportions. Let it sit for about a week or a little more, then you can make applications or simply lubricate the affected area.
Why is a keloid dangerous?
A colloidal scar is not dangerous to human life and health, but it can cause a lot of discomfort and significantly reduce the quality of life. In severe cases, the keloid grows quickly, occupying large areas of the body, and often recurs. When it is damaged, bleeding develops, since there are many blood vessels in the scar. In people with weakened immune systems, an infection that gets into the keloid tissue can cause an inflammatory process.
Particular discomfort is caused by keloids formed in women as a result of cuts and tears in the perineum during childbirth. This growth causes quite severe pain and leads to disruption of sexual life. Therefore, if a woman is prone to the appearance of scars during pregnancy, she should regularly massage the perineum, and then resort to magnetic wave therapy procedures to prevent keloids.
Causes of keloids
Keloids are formed under the influence of external and internal factors on the skin. The causes of colloid scars are varied.:
- Burns (chemical and thermal);
- Hormonal disorders. Pregnancy can also cause this type of scar. This is due to changes in hormonal levels;
- Wounds and abrasions;
- Decrease in the body's defenses due to chronic pathology. Often true keloids occur in people with tuberculosis;
- Incorrect suturing of the wound;
- Removal of moles, papillomas;
- Hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of massive connective tissue formations;
- Furunculosis and severe acne;
- Disruption of the processes of formation (strengthening) of connective tissue and collagen fibers.
Prevention
Preventive measures to avoid the appearance of a colloid scar:
- Do not scratch or injure the scar formed at the wound site;
- Use special postoperative bandages made of compression knitwear;
- Treat injured skin with anti-scarring agents: “Sledotsit”, “Kontraktubeks”, “Rescuer”.
- If you have previously developed keloids, then avoid piercings, tattoos and injection cosmetic procedures.
Diagnosis
There is no problem in diagnosing the occurrence of this problem. Any specialist in the field of dermatology or surgery, with a standard initial examination, will be able to do this with the naked eye, based on the external history and comments of the patient.
After this, an effective course of therapy is selected, and if this does not bring any results, then one of the methods of disposal is often recommended.

Creams, ointments, gels
Among the external preparations for the treatment of scars are those well known to many TV viewers: “Kontraktubeks” (ointment), “Lioton” (gel). There is also Kelofibrase (cream), hydrocortisone ointment (1%), Spenco (silicone gel pads), Mepitel (adhesive absorbent coatings with silicone), Zeraderm Ultra (cream that forms a protective film on the skin), Scarguard (liquid that protects skin from irritation and at the same time creating pressure on it).
The essence of using pressure bandages, pads, creams and liquids that form a pressure film on the skin is to slow down the growth and development of scar cells using compression. To achieve a positive result, these funds must be used for a long time (several months). What result can be achieved this way? The scar will become flat, paler, and the pain and itching in its area will disappear.
Causes of primary (spontaneous) scars
Spontaneous colloids form for no apparent reason. Old injuries may not be completely cured, although the skin in their place is no different from healthy ones. In this case, the formation of scars can be caused by disturbances in the functioning of the organs and systems of the body, as well as various infectious diseases. Doctors associate the appearance of colloids with a person’s predisposition to seborrhea. This is due to the fact that scars usually appear in places characteristic of seborrhea: the neck, shoulder blades, chin, ears and décolleté. Multiple scars can occur as a result of a genetic predisposition.
Photos before and after the procedure
Types of scars, difference from hypertrophic ones
The scar may be shaped like a star, a fan, or linear. Scars rarely grow on the face. Most often, raised scars can be seen on the chest, neck and shoulders. There are cases of complications in the form of keloids after ear piercing.
There are also old and young colloid scars. Keloids under five years of age are considered young. They are usually smooth and shiny. Old keloid scars are usually bluish, wrinkled and uneven.
Hypertrophic scars are similar in appearance to colloid scars, but do not extend beyond the wound, become comparable to the surface of the skin without treatment in about a year, and do not hurt or itch.
Physical impact
The patient may be prescribed one of the following treatment methods:
- Surgical excision of pathological tissues. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the open wound does not get infected.
- Radiation therapy is used very rarely due to the risk of developing cancer in the future. This method is used after surgery, the procedure is carried out four times over two weeks.
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen. The doctor conducts three therapy sessions. This method of treatment gives good results.
- Laser therapy has the advantage that healthy tissue is not injured. But often such treatment leads to the development of relapse of the pathology, since the laser affects only the superficial layer of the scar.
- Electrophoresis is used at the initial stage of pathology development.
Secondary keloids
Secondary keloids are formed as a result of injuries, as well as various thermal or chemical burns of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. In certain cases, a pathological formation is formed at the site of a former boil, stoma or trophic ulcer.
In addition, the colloidal scar (pictured) can be classified by age. A distinction is made between old scars and recently formed ones. Young keloids have a pronounced bright color and a glossy smooth surface. Old scars are distinguished by a large number of connective tissue nodes, pale color and roughness. A few years after formation, scars stop growing in size.

Colloid scars should be distinguished from other skin neoplasms. In cases where the emerging growth has a soft consistency, quickly increases in size and is accompanied by swelling of nearby tissues, then there are certain reasons to suspect the development of a malignant tumor process.
Let's sum it up
- Colloid scars and keloid scars are different names for the same disease.
- The keloid scar grows in different directions, is convex, hurts and itches.
- A hypertrophied scar is similar to a colloid scar, but it does not extend beyond the skin damage, can go away on its own and usually does not hurt.
- Science has not established the exact cause of the appearance of a keloid scar.
- Treatment of colloid scar requires a long time.
- It is impossible to completely remove a scar.
- Any damage to the skin can trigger the formation of a colloidal scar.
- Keloid scars are treated with external agents (creams, ointments, gels, compresses, silicone pads), interferon injections, steroid injections, surgery and radiation.
- A colloidal scar is not an oncological disease, but a benign tumor, a skin defect that causes physical discomfort and forms psychological complexes.
- The formation of a pathological scar is easier to prevent than to treat.
The causative factors for the formation of primary keloid scars are:
- completed injuries that are not visible on the surface of the skin;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pregnancy;
- infectious diseases in chronic form (tuberculosis, etc.);
- hereditary cause.
The causative factors for the formation of secondary keloid scars are:
- injuries of varying intensity.
- poor-quality removal of warts and moles.
- comedones.

Consequences

Many people are wondering whether colloidal scars are dangerous for the body? No, they are completely safe, and they get rid of this defect for purely aesthetic reasons. Discomfort may occur if the formation appears on joint bends and in places subject to constant friction.
In some situations colloid scars tighten fabrics and skin, so they have to be hidden with clothing.
But malignant tumors can develop from these formations if radiation therapy is not promptly applied.
Disease prevention
In order for the colloid scar to heal successfully, it is necessary to apply a number of measures.
- The use of bandages is mandatory to ensure that there is constant pressure on the damaged area.
- Under no circumstances should you self-medicate using aggressive agents such as vinegar and the like.
- If small-sized pustules appear on the neoplasm, under no circumstances should they be squeezed out, but it is better to immediately seek help from a specialist.
- Self-massaging of the tumor is excluded.
- There is no need to abuse high temperatures: solariums, saunas and anywhere where the scar can overheat.
- Do not immediately use products containing heparin, such as Contractubex, immediately after healing.
- Avoid infection, wounds and tension around the tumor.
Feature
The main characteristic feature of colloidal scars is the minimal relationship between the size of the scar and the severity of the initial skin injury. In most cases, scars form at the site of minor abrasions and scratches, acne, injections, and insect bites. In some people, for also unknown reasons, keloids form in areas of completely healthy skin. In this case, scars most often form on inactive areas of the body, for example:
- In the navel area, on the stomach.
- Behind the ears and on the lobes.
- On the shoulders and shoulder blades.
- On the chest, neck and collarbone area.
- At the base of the neck.
Briefly about further skin care
It is important to wash and moisturize the defect site in a timely manner.. Thanks to this, the renewal of koi cells will occur faster and regeneration will accelerate. Every time you shower, you should thoroughly moisturize your skin; it is better if you use organic products: olive, coconut, sea buckthorn oils.
In the modern world, a keloid scar is far from a stigma that a person, having received once, is obliged to bear throughout his life. A large number of clinics and private specialists are ready to help with a specific method and get rid of an unpleasant defect. The main thing is not to delay the healing process of the keloid for a long time and contact a specialist in time.
A keloid scar is the result of an excessive increase in connective tissue that occurs at the site of skin fusion during the postoperative period.
Most doctors agree that the appearance of such scars is caused by a violation of the mechanism of connective tissue structure in the human body and excessive production of collagen.
Violation of the integrity of the skin is fraught with several types of scars:

 Keloid scars arethe result of the growth of skin tissue over the surface of a healing wound, in which a tumor-like formation occurs on the skin.
Keloid scars arethe result of the growth of skin tissue over the surface of a healing wound, in which a tumor-like formation occurs on the skin.
A keloid scar is a smooth formation with a dense structure and evenly defined edges. The growth has a red, bluish or purple tint, which is explained by the growth of small capillaries into the skin. The boundaries of the keloid are located far beyond the edges of the wound itself and differ sharply from the surrounding tissue.
Keloid scars can interfere with movement. This is a particularly common problem when a formation occurs in the area of a joint or facial muscles.
The formation of a keloid scar is accompanied by pain. This may include tingling, burning, itching and occasional pain. The danger of such a growth is the high probability of relapse after treatment and the high ability to constantly grow.
What causes and how do keloid scars form on the body, head, face, ears
Keloid formation begins after the first restoration of the skin due to injury. At the site of a healed wound or cut, small compactions begin to appear, accompanied by discomfort. The seals increase, going beyond the scar, and acquire clear contours.
 A keloid scar is finally formed within a period of several weeks to several months. The following factors are identified that increase the likelihood of their occurrence:
A keloid scar is finally formed within a period of several weeks to several months. The following factors are identified that increase the likelihood of their occurrence:
- hereditary predisposition;
- wound infection;
- unstable hormonal levels;
- incorrect alignment of the cut edges;
- strong skin tension in the cut area;
- pregnancy;
- insufficient wound care;
- problems with immunity.
The tumor occurs due to an imbalance in the production of collagen and elastin.
Normally, they are provided by fibroblast cells and lead to wound healing. When the border of the injured skin is violated, collagen fibers grow and cause the appearance of a scar.
Exposed areas of skin are considered the most vulnerable to the development of a keloid scar. This area is the ears, neck, chest, upper back, face and shoulders.
Scars after mole removal
A keloid can form at the site of mole removal as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the body and improper care of the injured area.
 The place where the mole was previously located will become dense and a reddish tint will appear. Itching and burning may occur. At the first suspicion, you should contact a specialist.
The place where the mole was previously located will become dense and a reddish tint will appear. Itching and burning may occur. At the first suspicion, you should contact a specialist.
Scars after rhinoplasty
Keloids after rhinoplasty are often the result of improper skin care. The nasal area is characterized by a tendency to develop inflammation. Having experienced stress from surgery, the skin often changes its type, and the sebaceous glands begin to work more actively.
 To prevent scarring, you should follow your doctor’s recommendations and use antiseptics. It is worth noting that the risk of developing a keloid scar during repeated surgery is much higher. This is explained by the fact that the operation is performed on tissues that are initially injured.
To prevent scarring, you should follow your doctor’s recommendations and use antiseptics. It is worth noting that the risk of developing a keloid scar during repeated surgery is much higher. This is explained by the fact that the operation is performed on tissues that are initially injured.
Scars after blepharoplasty
Blepharoplasty is used to get rid of fine wrinkles, bags under the eyes and other cosmetic imperfections in the upper and lower eyelids. In this case, a keloid scar is one of the rare negative outcomes, since the procedure is performed with small incisions in the skin.
 If you are prone to the appearance of keloids, your doctor will prescribe additional treatment. In this case, applying a special silicone bandage to the injured area will be effective.
If you are prone to the appearance of keloids, your doctor will prescribe additional treatment. In this case, applying a special silicone bandage to the injured area will be effective.
Scars after mammoplasty
A keloid scar is one of the possible disorders of skin healing after mammoplasty. Small stitches remain in any case, but during normal healing they become invisible.
 To prevent the occurrence of keloid and proper tissue fusion, you should wear special compression garments for 6 weeks after surgery.
To prevent the occurrence of keloid and proper tissue fusion, you should wear special compression garments for 6 weeks after surgery.
Scars after biorevitalization
Biorevitalization is considered one of the methods for treating certain types of scars.
Efficiency is achieved by performing biorevitalization in conjunction with laser procedures. Injections accompany tissue healing after laser resurfacing.
As a rejuvenating procedure, biorevitalization is contraindicated for people prone to the formation of keloids, since even a small violation of tissue integrity, but in large quantities, can cause scars.
Scars after piercing
The likelihood that skin healing will result in a keloid scar is quite high among piercing enthusiasts. This is due to genetic predisposition and improper care of the puncture site.
The growth of the keloid is also provoked by the piercing jewelry, which creates additional tension. In addition, the earring creates friction against the skin, which also negatively affects healing.
 If complications occur, it is recommended to remove the jewelry and undergo a course of restorative procedures. The areas most at risk are the nose, eyes and lips.
If complications occur, it is recommended to remove the jewelry and undergo a course of restorative procedures. The areas most at risk are the nose, eyes and lips.
Scars after acne, pimples
Even an ordinary pimple can cause a keloid scar if there is a predisposition to it. People with dark skin are more likely to experience this problem. Acne marks increase in size and become keloids a month after initial healing.
 They usually appear in large numbers but are small in size. The diameter of each keloid is on average 4 mm, but can increase over time.
They usually appear in large numbers but are small in size. The diameter of each keloid is on average 4 mm, but can increase over time.
Post-burn scars
As a result of the burn, a keloid scar can form. This is possible if there is a predisposition and the degree of skin damage is severe. A chemical or thermal burn leads to the formation of a keloid on any part of the body.
 A scar can be recognized a month after the wound has healed, when single lumps begin to appear in the burn area. The likelihood of complications is higher if a large area of skin is affected.
A scar can be recognized a month after the wound has healed, when single lumps begin to appear in the burn area. The likelihood of complications is higher if a large area of skin is affected.
How to remove keloid and hypertrophic scars after surgery. Laser removal. Reviews
The following methods are used to treat keloid scars:

To achieve a positive effect, the scar must enter the maturity stage and stop growing. To do this, the affected area is treated with hormonal drugs and ointments, as a result of which the scar loses color and becomes soft. Only ablative resurfacing that acts directly on the scar tissue is allowed.
Laser resurfacing “evaporates” the scar, making it less noticeable.
Patients note a decrease in keloid volume, loss of color and change in structure after the first procedure. During treatment, a tingling and burning sensation is felt, which is normal. If a large area is being treated, anesthesia should be used.
After laser treatment, the scar will require special care. The doctor will indicate the frequency of treatment with a disinfectant and healing cream. Chlorhexidine and Bepanthen are commonly used.
 A few days after the procedure, the scar area will become covered with a crust that cannot be removed. Experts disagree about this method of treatment, since the laser can provoke a relapse.
A few days after the procedure, the scar area will become covered with a crust that cannot be removed. Experts disagree about this method of treatment, since the laser can provoke a relapse.
Removal of keloid scars with liquid nitrogen – cryotherapy. Reviews
This treatment method is classified as a conservative type of scar correction. The procedure requires a nebulizer with liquid nitrogen, a cotton swab and an analgesic (if the scar is large).
 Before resorting to the procedure, make sure that it is a keloid scar
Before resorting to the procedure, make sure that it is a keloid scar The advantage of removing the scar with nitrogen is that the risk of wound infection is reduced. Low temperature kills skin microflora, preventing infection. If infection does occur, this can be judged by swelling and the appearance of redness on the scar.
After exposure to nitrogen, a formation appears in the form of a bubble with liquid, which should not be pierced independently. Patients notice an improvement in the appearance of the skin, a change in the size and brightness of the keloid. However, the scar does not completely disappear.
To achieve the result, it is necessary to apply liquid nitrogen to the keloid scar for 2-10 minutes with breaks for thawing.
Treatment of keloid scars - drugs, ointments, creams. Photos before and after
Drug treatment is used both as an auxiliary or preparatory therapy before another type of treatment, and as the main method of treatment.
Ointments and creams basically contain collagen of different origins, which creates a film on the surface of the skin. The film prevents moisture loss, moisturizing the surface of the keloid. At the same time, hydration promotes healing and normalization of processes in tissues.
"Diprospan"
The drug is available in 2 forms:
- suspension;
- injection.
It is a hormonal agent.
 To reduce the defect, the keloid scar is chipped once a month. This allows you to make it softer and reduce the brightness of the color. Doctors have differing opinions regarding the drug, since hormonal therapy can provoke changes in the body.
To reduce the defect, the keloid scar is chipped once a month. This allows you to make it softer and reduce the brightness of the color. Doctors have differing opinions regarding the drug, since hormonal therapy can provoke changes in the body.
"Kontraktubex"
The action of the gel is ensured by the following components:
- allantoin– relieves itching and burning during healing, normalizes pigmentation, softens scars, and also activates blood circulation in the affected tissue;
- heparin sodium– makes the structure of the scar less dense, saturates the tissue with moisture and has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- cepalin(onion extract) – inhibits the development of fibroblasts, preventing the formation of a scar and its growth.
 The gel should be applied 2-3 times a day, massaging the scar from the center to the edges. Treatment period is 3-6 months.
The gel should be applied 2-3 times a day, massaging the scar from the center to the edges. Treatment period is 3-6 months.
The drug received more positive reviews when treating acne marks. Patients were not able to significantly reduce their keloid size with this gel.
"Lidaza"
The drug “Lidaza” is based on hyaluronic acid, which fills cells and stimulates decay processes in scar tissue. In this case, there is no effect on the collagen-collagenase system.
Available in the forms of solution for internal use and powder for external use.
 The drug does not show any visible positive results in the treatment of keloid scars.
The drug does not show any visible positive results in the treatment of keloid scars.
"Solcoseryl"
"Solcoseryl" contains deproteinized dialysate from the blood of calves, which stimulates cell regeneration by supplying glucose and oxygen. The most popular forms of release are ointment and jelly. The concentration of the active substance in the jelly is higher.
 When treating the scar 2 times a day for several months, improvements in the appearance of the skin are noted. But this remedy will not completely remove the keloid.
When treating the scar 2 times a day for several months, improvements in the appearance of the skin are noted. But this remedy will not completely remove the keloid.
"Kenalog"
The keloid scar is almost completely removed with the drug "Kenalog". This is a drug that causes tissue atrophy. It is used as a course of injections at intervals of 1 month to six months. The full course of treatment depends on the age of the scar, its area and size.
 As a result of using the product, the scar becomes flat and similar in color to the skin.
As a result of using the product, the scar becomes flat and similar in color to the skin.
Patients who used this remedy noted a long-term positive effect.
"Dermatix"
Among the many remedies for scars, this drug stands out for its effectiveness. Available in the form of a gel and a gel-based bandage (fabric and silicone). It has a superficial effect due to the silicone in the composition, making the keloid scar flat.
 This is one of the few products that act on the surface of the skin without changes in the inner layer. A significant disadvantage is the high price of the drug (about 1600 rubles).
This is one of the few products that act on the surface of the skin without changes in the inner layer. A significant disadvantage is the high price of the drug (about 1600 rubles).
The effectiveness of using ointments and creams increases when applied under a compressive bandage for several hours.
How to cure keloid scars at home - treatment with folk remedies
Traditional medicine recommends the following methods for removing keloid scars:
- compresses from infusions of chamomile, fennel, St. John's wort;
- massage with sea buckthorn oil;
- rubbing fresh honey;
- lubricating the surface of the keloid with rosemary and tea tree oil. These oils are essential oils, so they should be used in combination with a base oil;
- compress of crushed cabbage leaves and honey.
The effectiveness of these methods has not been proven. They can be used as an addition to the main therapy in consultation with the doctor.
How to hide a keloid scar - tattoo, permanent makeup
A keloid scar can be hidden with a tattoo or permanent makeup. These methods involve printing a long-term pattern directly onto the problem area of the skin, thereby masking the aesthetic defect.
 Tattooing needs to be renewed periodically so that the scar is not noticeable in the future, and tattoos accompany a person for the rest of his life.
Tattooing needs to be renewed periodically so that the scar is not noticeable in the future, and tattoos accompany a person for the rest of his life.
What is a keloid scar and how to get rid of it: video
What causes keloid scars and how to combat them - expert recommendations:
What is this, a keloid or hypertrophied scar? Doctor's explanation:
A keloid scar is an unpleasant cosmetic problem, the solution to which lies in comprehensive, competent treatment. The best result is achieved by a combination of active treatment methods (laser, cryotherapy, physiotherapy) and local exposure to medications (ointments, creams and injections).